Eating Disorders and Body Image in the Digital Age
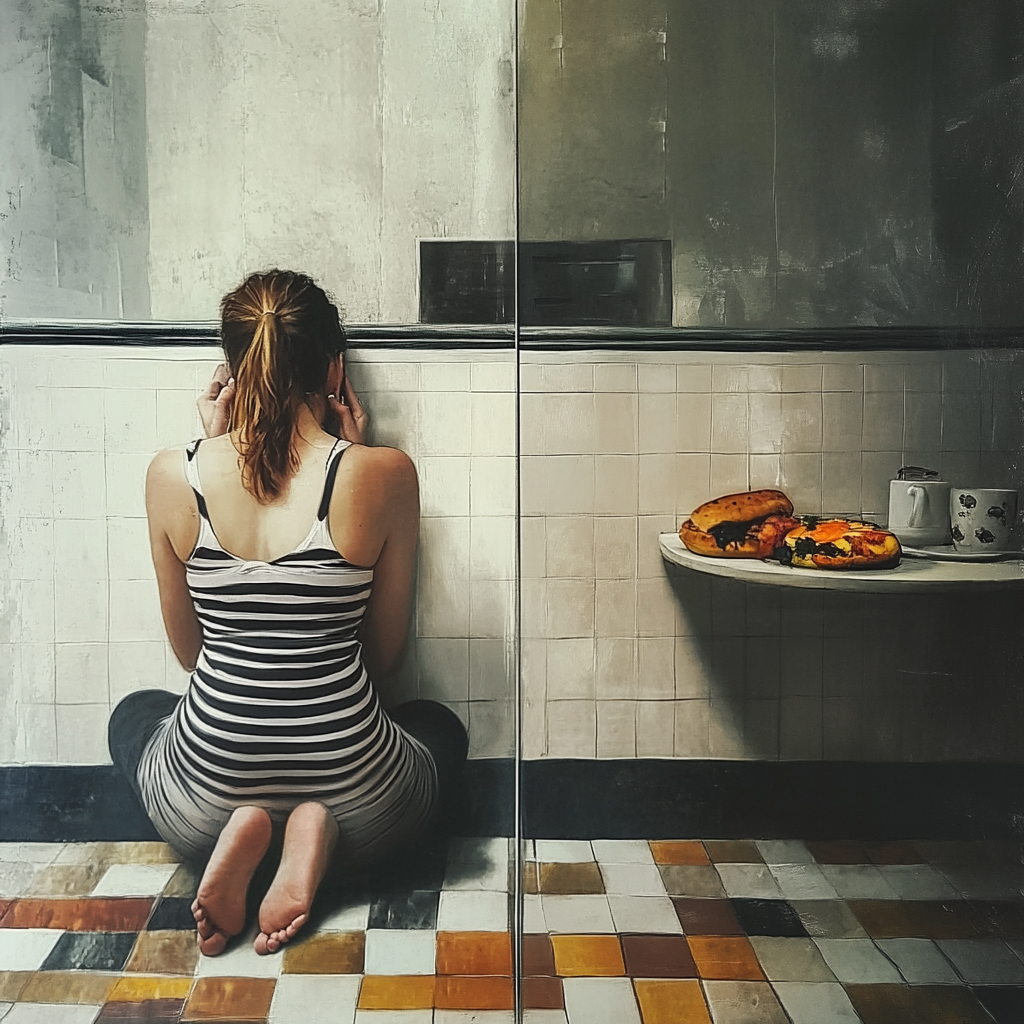
Most individuals, especially teens and young adults, grapple with eating disorders exacerbated by the pressures of social media and unrealistic body standards. As you navigate a world filled with filtered images and a pervasive culture of comparison, it’s vital to recognise the signs and risks linked to eating disorders and body image. In this blog post, you’ll learn about the various types of eating disorders, their impacts on health and well-being, and the avenues available for support and treatment.
Key Takeaways:
- Eating disorders have seen a notable increase among teenagers and young adults, influenced significantly by social media platforms and the pervasive culture of comparison.
- Common types of eating disorders include anorexia, bulimia, and binge eating disorder, each with distinct symptoms and health implications.
- The impact of media exposure on body image, alongside factors like trauma and perfectionism, plays a vital role in the development of eating disorders.
- Effective treatment options are available, including specialized eating disorder clinics, family-based therapy, and nutritional rehabilitation programs.
- Preventative measures, such as open discussions about body image and fostering a supportive environment at home, can help mitigate the risks associated with eating disorders.
What Are Eating Disorders?
For many, the struggle with eating disorders (EDs) is a complex and overwhelming journey. These disorders not only affect your physical health but also significantly impact your emotional and psychological well-being. Understanding eating disorders is the first step to recognizing the signs and seeking help.
Definition and Overview
Eating disorders are serious mental health conditions characterized by an unhealthy focus on food, body weight, and body shape. They can manifest in various ways and often result in severe health complications if left untreated.
Types of Eating Disorders
At least three primary types of eating disorders affect both teens and adults, and recognizing them is crucial for understanding your situation:
| Type | Overview |
|---|---|
| Anorexia Nervosa | Characterized by severe food restriction and intense fear of gaining weight. |
| Bulimia Nervosa | Involves episodes of binge eating followed by purging to prevent weight gain. |
| Binge Eating Disorder | Frequent episodes of eating large quantities of food without compensatory behaviors. |
| EDNOS (Eating Disorder Not Otherwise Specified) | A category that includes various eating disorders that do not fit specific criteria. |
| Pica | Characterized by the consumption of non-food items such as dirt or chalk. |
Any understanding of eating disorders, including their symptoms and behaviors, is vital for those affected or for those looking to support individuals in distress.
Understanding the complexity of these disorders involves looking closely at their underlying causes and varying manifestations. Each type has unique signs and symptoms, but all require immediate attention to ensure a healthy recovery:
| Type | Behavioral Signs |
|---|---|
| Anorexia Nervosa | Severe weight loss, distorted body image, and extreme calorie restriction. |
| Bulimia Nervosa | Binge eating, followed by feelings of shame, guilt, and compulsive purging. |
| Binge Eating Disorder | Recurring episodes of eating large amounts of food with no control. |
| EDNOS | Symptoms of eating disturbances that do not meet full criteria for other disorders. |
| Pica | Ingesting inedible substances consistently over a period. |
Any engagement with this information can help you or someone you care about identify potential eating disorders and take the necessary steps towards getting help.

Impact of Social Media on Body Image
There’s a significant connection between social media use and body image issues. With the rise of platforms showcasing curated lifestyles and edited images, you may find yourself comparing your appearance to unrealistic standards. This heightened scrutiny can lead to self-doubt and may exacerbate feelings of inadequacy, contributing to the development of eating disorders among both teens and young adults.
The Role of Online Platforms
Between the various online platforms available today, users are constantly bombarded with images that often depict an idealized version of beauty. Algorithms further personalize your experience, perhaps leading you to engage even more deeply with content that can impact your self-esteem and body image negatively.
Comparison Culture and Its Effects
Across social media, comparison culture thrives, fueling your insecurities about appearance. When scrolling through feeds filled with filtered photos, you may internalize these ideals, possibly leading to body dissatisfaction and unhealthy behaviors. This culture promotes unrealistic expectations that can trigger eating disorders, affecting both mental and physical health.
Statistics on Comparison Culture
| Impact of Social Media on You | Statistics |
| Reported dissatisfaction with appearance | 70% of young women |
| Increased anxiety and depression | 25% higher among frequent users |
For instance, studies indicate that the more time you spend on platforms that celebrate idealized beauty, the more likely you are to develop body image concerns. These platforms can foster feelings of inadequacy and lead to unhealthy behaviors such as disordered eating. It’s important to be mindful of how frequent exposure to these images can warp your self-perception and influence your mental health, highlighting the need for a balanced online experience.
Consequences of Constant Comparison
| Emotional Reactions | Resulting Behaviors |
| Increased feelings of inadequacy | Potential for disordered eating |
| Heightened anxiety | Withdrawal from social interactions |
Signs and Health Risks
Despite the stigma surrounding eating disorders, it’s important to recognize the alarming signs and health risks involved. Increasingly, individuals, particularly teens and young adults, experience adverse effects on their mental and physical well-being due to disordered eating habits and body image concerns. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes, making it vital to stay informed about the indicators of these conditions.
Recognizing Symptoms
An early recognition of symptoms is key to addressing eating disorders effectively. Look for significant changes in eating patterns, drastic weight loss or gain, withdrawal from social situations, and heightened preoccupation with food, body weight, and exercise. If you notice these behaviors in yourself or someone you care about, seeking help is vital.
Physical and Mental Health Consequences
Across the spectrum of eating disorders, both physical and mental health consequences can be severe and life-threatening. The effects go beyond immediate weight concerns, often leading to chronic health issues such as heart problems, gastrointestinal complications, and osteoporosis. Mentally, individuals may struggle with anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem, creating a challenging cycle of emotional turmoil. Early recognition and intervention are important to alleviating these severe outcomes and promoting helpful, supportive paths toward recovery.
Consequences of untreated eating disorders can escalate quickly. You may face both physical issues, such as organ failure, hormonal imbalances, and a weakened immune system, as well as mental health challenges, including severe depression and suicidal thoughts. Less obvious challenges, such as social isolation and strained relationships, can also emerge, making recovery increasingly difficult. Timely intervention and comprehensive treatment can mitigate these risks, emphasizing the importance of seeking help as soon as signs appear.
Teenage Girls and Boys: A Hidden Crisis
Now more than ever, eating disorders are affecting teenagers, with a significant rise among both girls and boys. The pressures of social media, including distortion of body image and constant comparison, heighten the risk of developing unhealthy eating behaviors. This hidden crisis requires your attention, as awareness can lead to early intervention and support for those struggling.
Prevalence Among Adolescents
Above 1.25 million people in the UK are estimated to be living with an eating disorder, with a staggering percentage being adolescents. Studies reveal that between 10-20% of teenage girls and boys experience symptoms of eating disorders, making it imperative for you to recognize the signs and find resources for help.
Unique Challenges Faced by Boys
Girls often dominate discussions around eating disorders, but boys face unique challenges that significantly affect their mental health. To combat societal stereotypes, boys may underreport their struggles or feel pressured to embody a particular physique. The rising focus on muscularity, combined with *media exposure* and *peer comparisons*, can lead you towards dangerous behaviors, such as excessive exercise and disordered eating practices, to achieve an idealized body image.
Treatment and Recovery Options
Not all hope is lost when dealing with eating disorders; effective treatment and recovery options are available. It’s crucial to consult with healthcare professionals who specialize in eating disorders. Treatments often include a combination of therapy, nutritional support, and in some cases, medication. Early intervention is key to overcoming the challenges associated with these disorders, and many individuals can achieve recovery with the right support.
Approaches to Therapy
Before submerging into treatment, it’s helpful to understand the various therapeutic approaches available. Therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) focus on changing negative thought patterns related to body image and eating behaviors. Family-based therapy engages family members in the recovery process, which can be especially beneficial for adolescents. Ultimately, the right approach will depend on your unique situation and the severity of the disorder.
Support Systems and Resources
Across the UK, a variety of resources and support systems exist to help you navigate the challenges of eating disorders. Support groups like Beat provide a platform where you can connect with others sharing similar experiences, fostering an environment of understanding and encouragement.
Another vital resource is professional guidance through therapists and clinics specializing in eating disorders, where you can access personalized treatment plans. Integrating support from friends and family is equally important in your recovery journey. By utilizing these support systems and resources, you not only enhance your chances of recovery but also create a community that advocates for your wellness and encourages a healthier relationship with your body.
Preventative Steps for Families
Unlike many issues, eating disorders can often be addressed through proactive measures within the family unit. By fostering a supportive and affirming home environment, you can help your loved ones develop healthier relationships with food and self-image. Engaging in open discussions about body image and the impact of social media can create a safe space for sharing feelings and concerns, ultimately reducing the risks associated with eating disorders.
Promoting Healthy Body Image
Across various platforms, you can encourage positive body image by championing diverse and realistic representations of beauty. Highlighting the importance of self-acceptance and celebrating individuality can help counteract the negative influences of online filters and comparison culture. Share messages that prioritize health over appearance, and actively challenge societal standards that may contribute to body dissatisfaction.
Open Communication and Support
Steps to nurturing open communication and support include establishing regular family check-ins where everyone can share their thoughts and feelings. This practice allows you to identify early signs of distress and encourages your loved ones to speak up about their struggles. Indeed, fostering this environment of understanding and empathy can empower your family members, reducing the likelihood of developing eating disorders.
Being attentive to changes in behavior, such as food rituals or withdrawal from social activities, is imperative. Offer reassurance and remind them that their worth is not tied to their appearance, encouraging a dialogue around feelings rather than focusing solely on weight or looks. By maintaining open lines of communication, you strengthen your family’s resilience against societal pressures and promote healthier emotional health.
Final Words
On the whole, understanding the complexities of eating disorders and body image in the digital age is vital for you and your loved ones. Acknowledging the impact of social media on self-perception can empower you to seek help or support someone in need. By fostering open conversations and encouraging positive body image, you can contribute to a healthier environment. Whether you’re navigating your own challenges or supporting someone else, awareness and compassion are key elements in combatting these issues and promoting recovery.
FAQ
Q: What are the most common types of eating disorders?
A: The most common types of eating disorders include anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge eating disorder. Anorexia involves extreme restriction of food intake and an intense fear of gaining weight. Bulimia is characterized by cycles of binge eating followed by purging behaviors, such as vomiting or using laxatives. Binge eating disorder involves episodes of consuming large quantities of food without compensatory behaviors, often leading to feelings of guilt or shame.
Q: How does social media contribute to body image issues?
A: Social media can significantly impact body image by promoting unrealistic beauty standards through edited photos and curated lifestyles. Users may engage in unhealthy comparisons, leading to feelings of inadequacy or lower self-esteem. The constant exposure to idealized body types can fuel dissatisfaction with one’s own body, potentially triggering or exacerbating eating disorders.
Q: What are some signs that someone may be struggling with an eating disorder?
A: Signs of an eating disorder can vary but often include drastic weight loss or gain, avoidance of social situations that involve food, excessive exercise, extreme preoccupation with body size or shape, and changes in eating habits. Emotional symptoms may include anxiety, irritability, or withdrawal from family and friends. If these behaviors are noticed, it is important to approach the individual with care and encourage them to seek professional help.
Q: How can families help prevent eating disorders?
A: Families can take preventive steps by fostering a positive body image, modeling healthy eating habits, and encouraging open discussions about body image and self-esteem. It’s imperative to promote the idea that worth is not tied to appearance and to challenge societal beauty standards. Additionally, encouraging children and teenagers to explore various hobbies and interests can build their confidence and self-identity beyond physical appearance.
Q: What treatment options are available for those with eating disorders?
A: Treatment for eating disorders typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, nutritional counseling, and medical support. Various approaches may include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), family-based therapy, and exposure therapy. In some cases, individuals might require inpatient or outpatient care at specialized eating disorder clinics. Nutritional rehabilitation is also imperative to restore healthy eating patterns and educate patients about balanced nutrition.